Clone app development is transforming how businesses enter competitive markets quickly and cost-effectively. If you’ve ever wondered how new apps launch with features remarkably similar to popular platforms, you’re witnessing clone app technology in action. This guide explains everything about app cloning meaning, why companies choose this approach, and how you can use it for your business.
What is clone app development? It’s the process of creating a mobile application that mirrors the core features and user experience of an existing successful app while customizing it for your specific audience. Businesses, founders, and developers turn to clone app development because it reduces risk, cuts development time, and provides a proven blueprint for success.
In this guide, you’ll learn the complete clone app development process, from initial planning through launch. You’ll discover the benefits, understand potential challenges, explore real-world examples, and get actionable steps to build your own clone app. Whether you’re a startup founder or an established business exploring new markets, this guide gives you the knowledge to make informed decisions about mobile app cloning.
What is Clone App Development?

Clone app development means creating an app that replicates features, user interface, user experience, and core functionality of a successful app while customizing it for a different audience or use case. Think of it as using a tested recipe but adding your own ingredients to make it unique.
This approach isn’t about creating illegal copies. Legal clone app development focuses on building differentiated products that use similar concepts without violating intellectual property rights. You’re inspired by proven models but create something distinct with your own branding, unique features, and specific value propositions.
Why does this matter? Because clone app development reduces development time and cost since the concept is already validated in the market. When you build a mobile app clone, you leverage tested user experience patterns that people already understand and enjoy. This means faster market entry and higher chances of user adoption.
Clone scripts provide the foundation for rapid development. These pre-built templates contain common functionalities that you can customize rather than coding everything from scratch. The clone app meaning extends beyond simple copying—it’s about smart adaptation of successful models to new markets or niches.
Why Businesses Consider Clone App Development
The benefits of clone apps extend across multiple dimensions, making them attractive for startups and established companies alike.
Reduced Development Time
When you choose clone app development, you’re working with an existing feature blueprint. The original app has already solved design problems, mapped user flows, and established what works. You don’t spend months debating which features to include—you start with a proven foundation. This shortens your development cycle from potentially 12-18 months down to 3-6 months in many cases.
Lower Cost
Building apps from scratch requires significant investment in research, design, and development. Clone script advantages include pre-built templates and frameworks that dramatically reduce initial investments. Instead of paying designers to create every screen and developers to code every feature from zero, you customize existing components. This can reduce costs by 40-60% compared to custom development.
Market Validation
Why build a clone app? Because the original app’s success validates market demand. When Uber proved ride-hailing worked, entrepreneurs could confidently build similar apps for their regions knowing the business model was viable. This reduced risk makes clone app development benefits particularly valuable for businesses entering new markets or testing concepts.
Opportunity for Customization
Despite using a proven model, you’re not locked into exact replication. Clone app development offers substantial room for differentiation. You can add unique features, modify workflows to match your target audience, incorporate different payment methods, or adjust the interface to reflect cultural preferences. This flexibility lets you benefit from a tested foundation while creating genuine competitive advantages.
Key Steps in Clone App Development Process
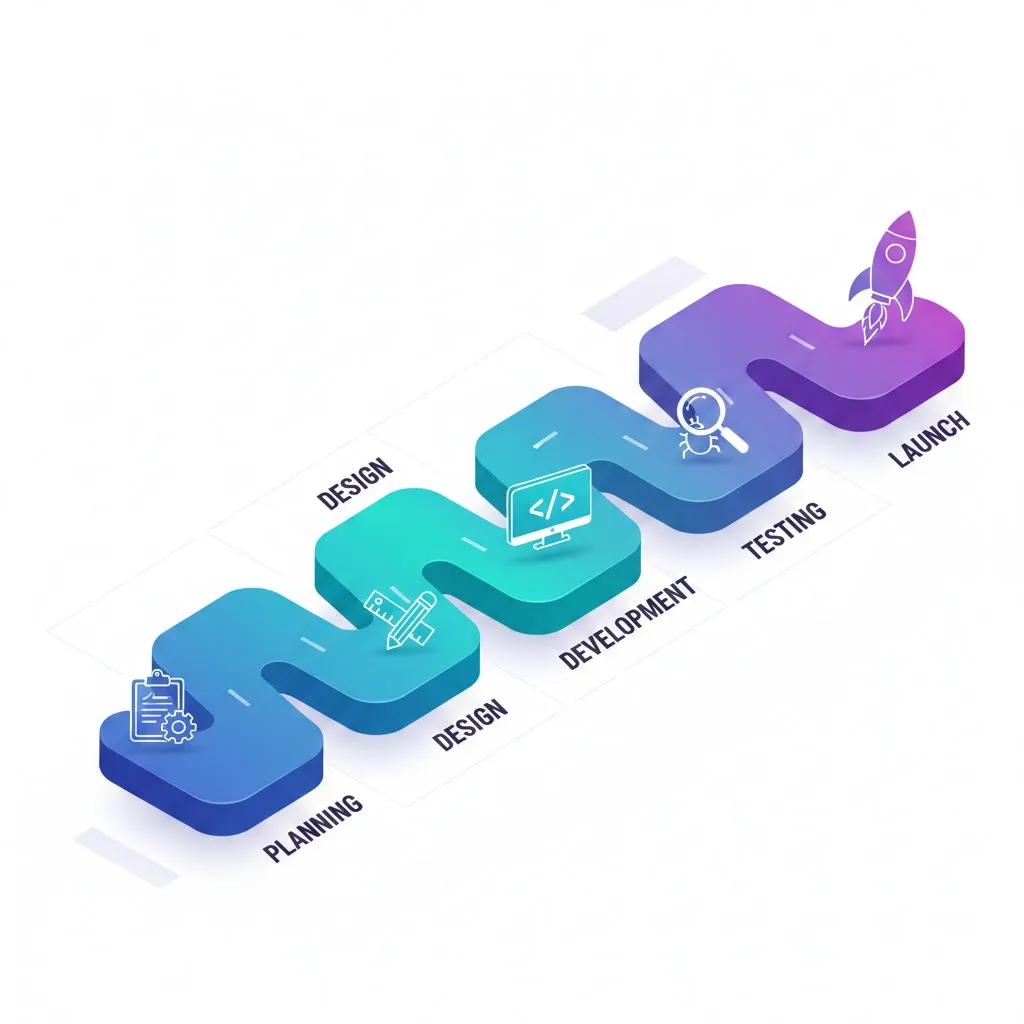
Step 1: Identify the App to Clone
App analysis forms the foundation of successful clone app planning. Start by selecting a popular app in your target niche. Don’t just pick any successful app—choose one that serves a market segment you understand or want to enter.
Conduct thorough competitor feature analysis. Document every feature the original app offers. Create spreadsheets listing functionality, user flows, screen layouts, and interaction patterns. Pay attention to what makes users love the app. Is it the seamless checkout? The intuitive navigation? The personalization features?
Study the app’s user interface style. Take screenshots, note color schemes, typography choices, button placements, and information hierarchy. Analyze user reviews to understand what people appreciate and what frustrates them. This research reveals opportunities for your clone to improve upon the original.
Step 2: Research and Requirement Gathering
Clone app requirements divide into essential features and optional enhancements. Essential features are the core functionalities that define the app category—a ride-hailing app must have driver-passenger matching, GPS tracking, and payment processing. Optional enhancements add value but aren’t strictly necessary for launch.
Document which custom features will differentiate your app. Maybe you’ll add subscription plans, loyalty rewards, or social sharing capabilities. Consider your target audience’s specific needs. If you’re building a food delivery clone for a specific city, you might need features for local payment methods or dietary preference filters that the original app doesn’t offer.
Create detailed app enhancements specifications. Write down exactly how each feature should work. Include user stories like “As a customer, I want to save favorite orders so I can reorder quickly.” This clarity prevents confusion during development and ensures everyone understands the vision.
Step 3: Legal Considerations
Clone app legal issues are critical to address before development begins. You must avoid copyright in clone apps violations while building your product.
Never duplicate proprietary assets. This means you cannot copy the exact icons, logos, images, color combinations, or specific design elements that are trademarked or copyrighted. Your app needs its own visual identity. Change branding completely—create your own name, logo, and brand colors. Modify the user interface enough that it’s clearly a different product.
Work with a lawyer who understands IP compliance in software development. They’ll help you understand which elements you can legally replicate (general features and workflows) versus what you must avoid (specific implementations, graphics, and branded content). Some jurisdictions have strict laws about UI/UX copying, so geographic location matters.
The line between inspiration and infringement exists but isn’t always clear. As a general rule, if someone could confuse your app with the original based on appearance alone, you’ve copied too closely. Focus on creating a similar experience with different execution.
Step 4: Design and Prototype
Clone app design requires balancing familiarity with originality. Use professional design tools like Figma or Adobe XD to create your interface mockups.
Start with wireframes—simple black and white sketches showing where elements appear on each screen. Map out complete UI clone app flows for every user action. How does someone sign up? What happens after they place an order? Where do error messages appear?
Move from wireframes to high-fidelity mockups with your actual colors, typography, and graphics. Focus on usability improvements. If the original app has confusing navigation, fix it in your design. If users complain about too many steps to complete an action, streamline your version.
UX clone app development means thinking about the entire user experience. Consider loading states, empty states, error messages, and success confirmations. Design for both first-time users who need guidance and returning users who want efficiency. Test your designs with potential users before coding begins. Show them mockups and watch how they interact. Their feedback reveals problems you can fix cheaply now rather than expensively later.
Step 5: Development
The clone app development process begins with choosing your mobile app tech stack. You face a fundamental decision: native development or cross-platform development.
Native development means building separate apps for iOS and Android. You’d use Swift or Objective-C for iOS and Kotlin or Java for Android. Native apps typically perform better and provide more polished user experiences, but they cost more and take longer since you’re essentially building two apps.
Cross-platform development uses frameworks like React Native or Flutter to build one codebase that runs on both iOS and Android. This approach is faster and cheaper while delivering good performance for most use cases. Many successful clone apps use cross-platform development to reach markets quickly.
Clone script customization provides your starting foundation. Pre-built clone scripts offer user authentication, database structure, API endpoints, and basic features already coded. Your development team customizes this foundation by adding your unique features, modifying workflows, integrating your chosen payment gateways, and adjusting the code to match your design.
Even with clone scripts, expect significant development work. You’ll need to implement custom logic, optimize performance, ensure security, handle edge cases, and integrate third-party services. Quality development takes time—rushing leads to bugs and poor user experiences.
Step 6: Testing
Clone app testing ensures your app works reliably before users see it. Comprehensive mobile app QA catches bugs that frustrate users and damage your reputation.
Device testing means checking your app on multiple phone models, operating system versions, and screen sizes. What works on the latest iPhone might break on a three-year-old Android device. Cross device testing reveals these compatibility issues.
Performance testing evaluates speed and responsiveness. Users abandon apps that feel slow. Test loading times, animation smoothness, and how the app handles poor internet connections. Monitor memory usage and battery drain—apps that overheat phones get uninstalled quickly.
API stability testing confirms that all your connections to backend servers, payment processors, mapping services, and other external systems work reliably. Test error handling by simulating failures. What happens when the payment gateway times out? Does your app crash or show a helpful error message?
UX testing involves real users completing common tasks while you observe. Watch where they get confused, where they hesitate, and where they fail. Their struggles reveal problems your team missed because you’re too familiar with the app.
Step 7: Launch and Feedback
App launch strategy determines early success. Don’t just release your clone app deployment to everyone simultaneously. Use a phased rollout starting with a small user group. This limited release lets you catch critical issues before they affect thousands of users.
Set up analytics tracking from day one. Tools like Google Analytics, Mixpanel, or Amplitude show how users actually behave in your app. Which features do they use most? Where do they drop off? How long do they stay engaged?
Implement crash monitoring with services like Crashlytics or Sentry. These tools automatically report when your app crashes, providing technical details your developers need to fix problems quickly.
User feedback collection must be systematic. Include in-app prompts asking users to rate their experience. Make it easy to submit bug reports or feature requests. Monitor app store reviews and respond professionally to both positive and negative comments.
Plan for iterative improvements. Your first release won’t be perfect. Use data and feedback to prioritize updates. Maybe users want a dark mode. Perhaps the checkout process needs simplification. Regular updates based on real user needs build loyalty and improve retention.
Challenges and Considerations in Clone App Development
Clone app risks require careful management throughout your project.
Legal Risks
Copying apps too closely creates clone app legal issues that can destroy your business. Using the same UI icons, identical color schemes, or similar names might violate intellectual property rights. Companies protect their brands aggressively. Even if you think your copying is legal, defending against lawsuits costs money and time. Always differentiate clearly. Change enough visual and functional elements that no reasonable person would confuse your app with the original.
Limited Customization
Clone script limitations can frustrate your ambitions. Pre-built scripts often use rigid architectures that make certain modifications difficult or impossible. You might want to add a sophisticated matching algorithm or real-time collaboration features, but the clone script’s foundation doesn’t support it. Before choosing a clone script, verify it can accommodate your planned customizations. Otherwise, you’ll waste money on a foundation you must replace.
User Trust
People sometimes distrust clone apps due to perceptions about authenticity and reliability. Why should they use your Uber clone instead of Uber itself? Users worry about data security, payment safety, and service quality with unfamiliar brands. Combat this through transparent communication about your security measures, clear privacy policies, responsive customer service, and building social proof through reviews and testimonials.
Technical Challenges
Technical issues in clone apps often center on integration complexity. Connecting your app to payment gateways, mapping services, SMS providers, email systems, and analytics platforms requires careful configuration. Each service has different APIs, authentication methods, and error-handling requirements. Cross-platform compatibility adds another layer—features that work perfectly on iOS might behave differently on Android. Budget extra time for integration work and cross-platform testing.
Market Competition
Many clone apps exist in popular categories like food delivery, ride-hailing, and dating. Standing out requires genuine innovation. Simply copying features isn’t enough when ten other companies already offer similar apps. Differentiation becomes essential for survival—you need unique value propositions that give users compelling reasons to choose your app over alternatives.
Examples of Popular Clone Apps

Real-world clone app examples demonstrate successful applications of this development approach.
Instagram Clones
Social media clones replicate photo-sharing, filters, stories, and social interaction features. These apps often target specific niches—maybe photographers, travelers, or local communities. They maintain core social networking functionality while adding specialized features or focusing on particular user groups.
Uber Clones
Ride-hailing clones dominate many regional markets worldwide. An Uber clone provides driver-passenger matching, GPS tracking, fare calculation, and payment processing. Successful versions differentiate through local payment methods, regional pricing strategies, better driver compensation, or additional vehicle types.
DoorDash Clones
Food delivery clone apps connect restaurants, delivery drivers, and customers. These apps replicate menu browsing, order placement, real-time tracking, and payment systems. Regional versions succeed by partnering with local restaurants, offering better delivery terms, or adding features like group ordering or meal planning.
WhatsApp Clones
Messaging clones provide text, voice, and video communication. They replicate core messaging functionality but often add enhanced privacy features, business tools, or integration with other services. Some focus on specific markets with features tailored to local communication preferences.
These examples show how clone apps maintain familiar core features while incorporating region-specific changes, different branding, and unique enhancements that provide genuine value to their target markets.
How to Differentiate Your Clone App

Custom clone app features separate successful apps from forgotten ones. Here’s how to stand out with a clone app through meaningful clone app innovation.
New Monetization Models
Instead of copying the original’s pricing, experiment with alternatives. Maybe offer a freemium model with premium features, implement subscription tiers with different benefits, or use transaction-based pricing that’s fairer for occasional users. Creative pricing can attract users frustrated with existing options.
Loyalty Programs
Reward repeat customers with points, discounts, or exclusive perks. Build community through VIP tiers that recognize your best users. Gamification elements like achievement badges or streak rewards increase engagement and retention.
Hyperlocal Features
Tailor your app to specific geographic markets. Support local payment methods, integrate with regional services, accommodate local languages and cultural preferences, or partner with local businesses. An app that feels designed specifically for a market beats generic international competitors.
Advanced Analytics
Give users insights the original app doesn’t provide. Maybe show spending trends, usage patterns, personalized recommendations based on behavior, or comparative statistics. Data-driven features add value while creating switching costs for users.
Superior Customer Service
Many clone apps in competitive markets differentiate through dramatically better support. Offer live chat, faster response times, local language support, or dedicated account managers for premium users. Excellent service builds loyalty when features are similar across competitors.
Community Features
Add social elements that bring users together. Forums, user groups, shared experiences, or collaborative features create network effects. When users build connections in your app, they’re less likely to switch to competitors.
Differentiation improves user trust and competitiveness by proving your app offers genuine advantages. Don’t just copy—improve and innovate based on your unique understanding of your target market.
Cost, Timeline, and Development Considerations
Clone app development cost varies significantly based on several factors.
Cost Factors
Your app development pricing depends on technology stack choices—native development costs more than cross-platform. Feature complexity matters—simple apps cost $20,000-$50,000 while complex apps reach $100,000-$300,000 or more. Third-party API integrations add expenses for mapping services, payment gateways, and analytics tools. Team composition affects costs—offshore developers charge less than local teams, but communication and quality vary. Design complexity impacts pricing—custom animations, illustrations, and sophisticated interactions require more design hours.
Timeline for Clone App
Typical development proceeds through distinct phases:
- Analysis and planning: 2-4 weeks for market research, feature definition, and technical planning
- Design: 3-6 weeks creating wireframes, mockups, and prototypes
- Development: 8-16 weeks building features, integrating services, and implementing business logic
- Testing: 3-5 weeks for QA, bug fixes, and performance optimization
- Launch preparation: 1-2 weeks for app store submission and final checks
Total timeline for clone app development ranges from 4-8 months for most projects. Clone scripts can shorten timelines by 30-50% since foundation code already exists. However, customization still requires significant time—just because you start with a script doesn’t mean development becomes automatic.
Budget realistically and include contingency funds for unexpected challenges. Rushed development produces buggy apps that frustrate users and damage your reputation. Better to launch slightly late with quality than rush to market with problems.
Conclusion
Clone app development offers businesses a strategic path to enter competitive markets with reduced risk and faster time to market. By leveraging proven concepts while adding meaningful customization, you can build your own clone app that serves your target audience effectively.
This guide covered the complete clone app development process—from understanding what clone apps are, through detailed development steps, to launch and differentiation strategies. You learned about key benefits including reduced costs and development time, market validation through proven concepts, and opportunities for customization. You explored critical challenges like legal considerations, technical complexity, and market competition.
Remember that successful clone apps aren’t just copies—they’re improved, differentiated products built on validated concepts. Focus on understanding your target market deeply, adding genuine value through unique features, ensuring legal compliance throughout development, and delivering excellent user experiences.
Whether you choose to build your own clone app for food delivery, ride-hailing, social networking, or any other category, informed decision-making and emphasis on customization separate winners from failures. Start with a proven foundation, but don’t stop there—innovate, improve, and create something users genuinely prefer over alternatives.
Your clone app development journey begins with clear strategy, thorough planning, legal awareness, quality execution, and commitment to continuous improvement based on user feedback. The market rewards apps that combine the familiarity of proven models with the innovation of fresh ideas.